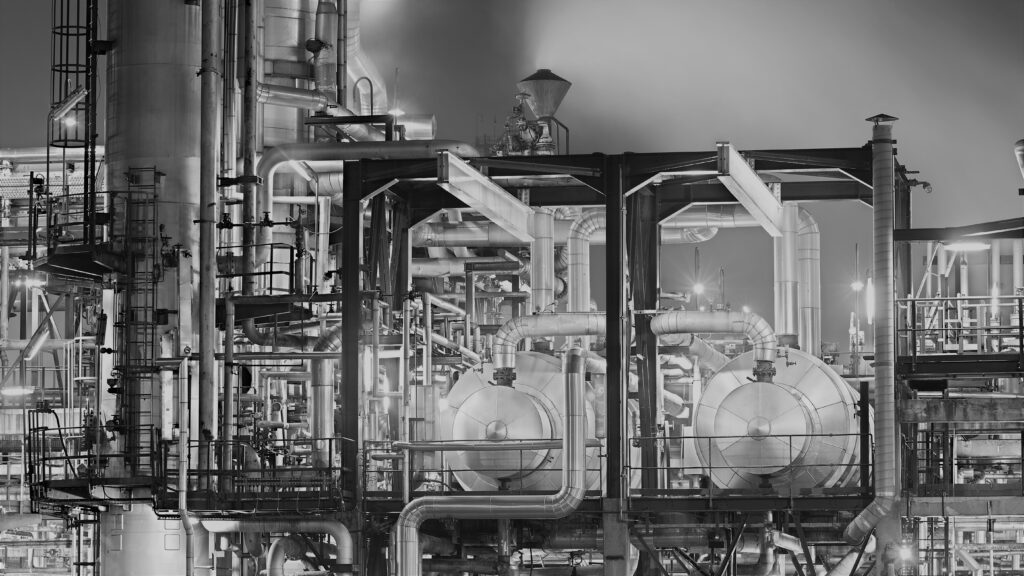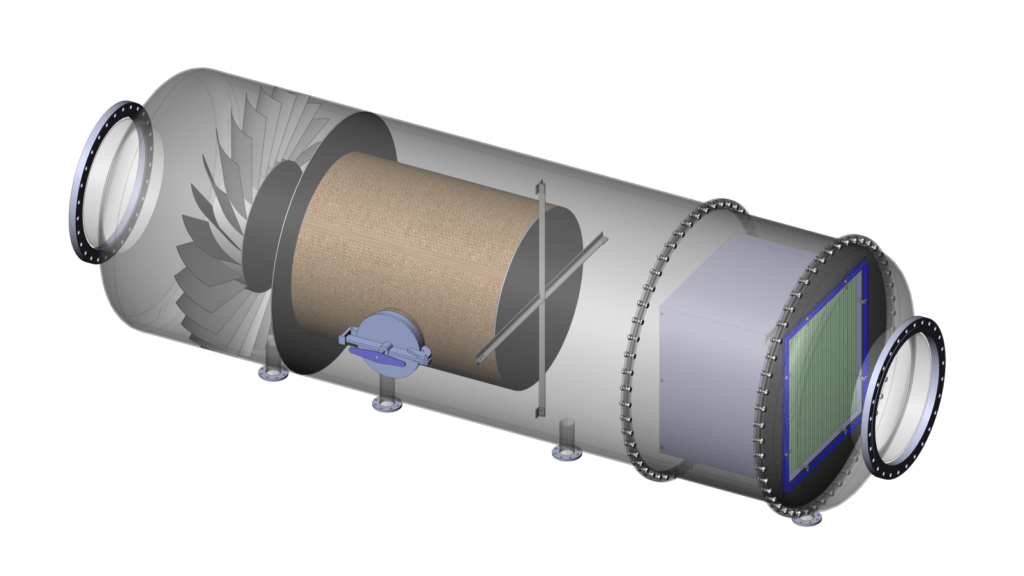
Entrainment Separator
Process Industries
Entrainment separator or mist eliminators are used separates mist from a gas or vapors stream to recover valuable products/by-products or to eliminate the undesirables. It improve product purity and protect downstream equipment. In process plants the vapors generated during evaporation/boiling from evaporator or evaporative crystallizers contains some entrained drops of boiling solution which is undesirable due to loss of that component. Limpid Entrainment Separator is a multi-stage separator which effectively arrests very fine drops i.e. up to 5μ, while total pressure drop very low i.e. maximum 2.0 kPa. First stage consisting of swirl generator to removes small size particles followed by candle mesh pad as second stage to remove further smaller particles. Third stages have vane-type arrangement to remove fine particles and then a polypropylene pad as forth stage to remove very fine particles from the liquid laden gaseous or vapor steam.
Max. ΔP2.0 kPa | Particle EliminationUp to 5μ | Separation Stages1 to 4 as per application |
Stripping Column
Pharma Industry
Stripping columns are used to strip of the volatile components from feed stream by altering boiling point using vacuum and with the application of added heat. Liquid produced after stripping is rich in less volatile components. Limpid Engineering offers packed column with random packing as stripping columns. It is used for waste water pre-treatment for the removal of odour in it. It remove traces of harmful contaminants like ammonia, benzene, methanol, ethanol, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate, and other VOCs from waste streams. Volatile organic compounds are sparingly soluble in water and can be easily removed with the help of waste steam & vacuum. Because of environmental considerations and regulations, these must be removed from wastewater before discharging out. We offer leading product in this segment.
PackingMetal Pall Rings | ConstructionSS 316/304 | Pressure DropOptimized |
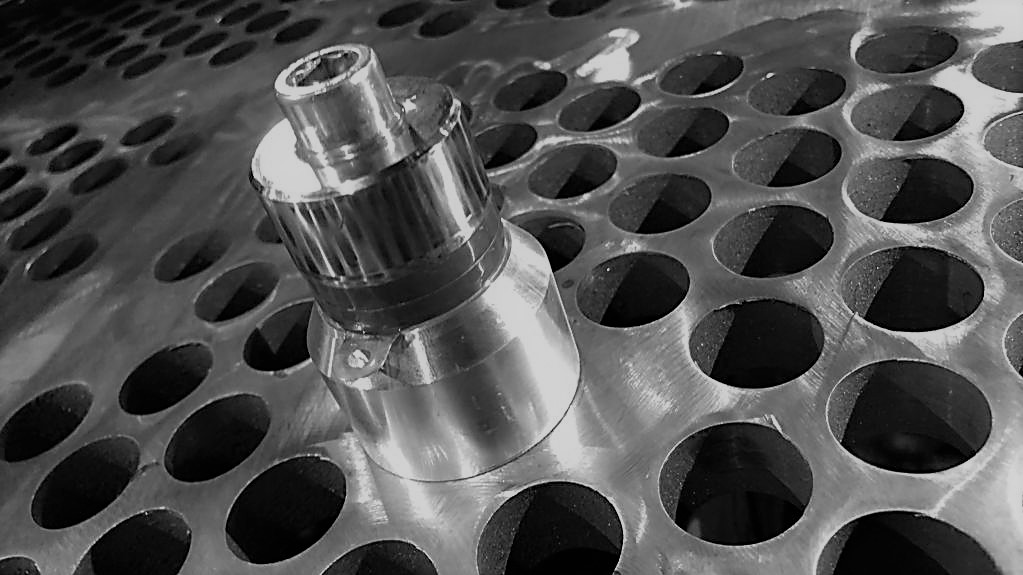


Ultrasonic CIP system
Process, Food, Pharma & Oil Refineries
Fouling/scaling of the heating surface of heat exchangers/evaporators/condensers is the bane of process industry. It not only causes corrosion of heating surfaces also restricts fluid flow and impairs heat transfer across the metal fluid interface. Scaling starts when a salt nucleus settles on the surface and subsequently salts precipitation from the liquid to grow bigger into scale. If scale is left untended, it will continue to accumulate and thicken, which can further damage the equipment and reduce its effectiveness. Thick layer of scale is difficult and costly to remove, which is why it’s important that action must be immediate. Limpid Engineering's ultrasonic CIP system absolutely prevent the scaling or fouling of the heating surface of the heat exchangers, evaporators/condenser and crystallizers. It is best and almost no cost method that maintain the equipment performance throughout life cycle without taking it offline for cleaning.
ConstructionSS 304 | ControlPLC/DCS Control | PackageOne Step solution |
Evaporator (Mechanical Vapors Compressor)
Pharma, Food & Process Industry
Vapor recompression is being used in many industrial applications as an alternative to direct steam utilization generated by burning fuel in boiler. Dairy, saline, pharma, other food and distillery industries are among that is using Mechanical vapor recompression, in particular, in industrial evaporators for concentration of solids. Waste heat from a spent vapor stream is upgraded to a higher pressure and then re-using it to capture its useful energy by simultaneously condensation and evaporation. The vapor generated from evaporator is compressed to increase pressure and corresponding temperature. As the pressure rises, the saturation temperature also increases along with some degree of superheat is added to compressed vapours. This increase in saturated temperature generates a temperature difference between the exhaust vapor and the working fluid. The temperature difference then enables heat transfer between the two fluid streams using a heat exchanger element. This arrangement usually employs a compressor to increase the pressure of the vapor stream carrying waste heat. Since energy of latent heat is always reused, the energy input needed for such a process is simply the energy supplied to compress the fluid. This process is very energy-efficient, and offers many unique advantages. Limpid Engineering's MVR based plate or tubular forced type evaporator is available in various MOCs to suite the liquid to handle to concentrate the liquid stream or to recover the solvent i.e. water in most of the cases.
ApplicationConcentration | ConstructionSS 316/304/Ti/Duplex | Energy EfficiencyHighly Efficient |

